Plant fertilizer numbers – what NPK ratios mean and why they are important
Fertilizers play a key role in making sure your plants are healthy. However, their packaging can be confusing so here is how to understand the jargon


Design expertise in your inbox – from inspiring decorating ideas and beautiful celebrity homes to practical gardening advice and shopping round-ups.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?
Twice a week
Homes&Gardens
The ultimate interior design resource from the world's leading experts - discover inspiring decorating ideas, color scheming know-how, garden inspiration and shopping expertise.

Once a week
In The Loop from Next In Design
Members of the Next in Design Circle will receive In the Loop, our weekly email filled with trade news, names to know and spotlight moments. Together we’re building a brighter design future.

Twice a week
Cucina
Whether you’re passionate about hosting exquisite dinners, experimenting with culinary trends, or perfecting your kitchen's design with timeless elegance and innovative functionality, this newsletter is here to inspire
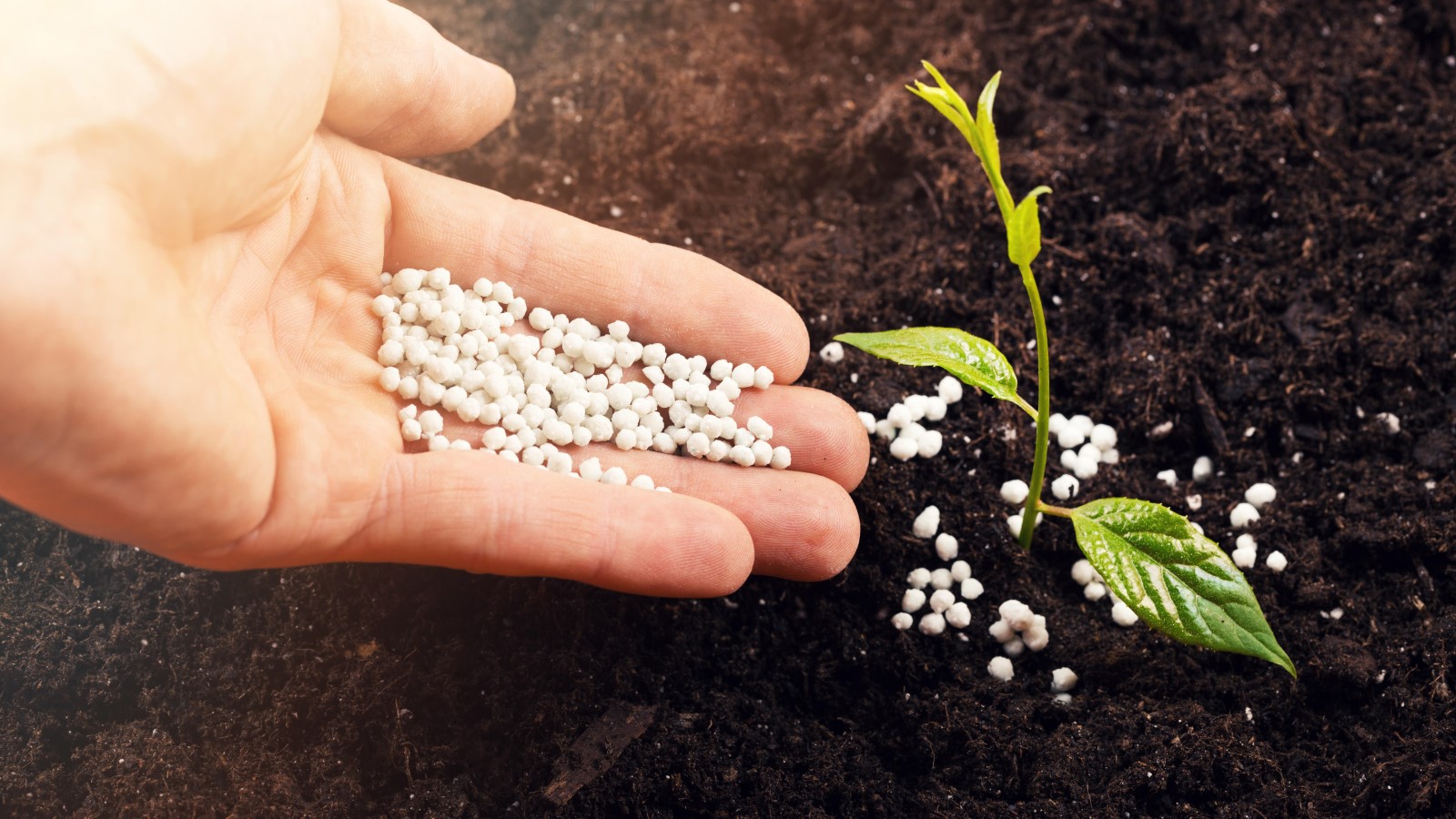
Q: I see lots of fertilizers in the garden centers and they all feature different numbers and references to their NPK. I find it all confusing. What exactly does NPK mean and how can I understand the plant fertilizer numbers on the packaging to make sure I get the right one for me?
A: Fertilizers are concentrated sources of important nutrients that are vital to help plants grow big and strong. They are typically added to the growing medium and made up of a combination of the major nutrients, nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium.
It can seem daunting but it is important to understand the plant fertilizer numbers you see on the packaging. Whether you want to fertilize a lawn, your vegetable garden, or your houseplants – the NPK explains the nutrient make-up of that fertilizer and how it can benefit your plants.
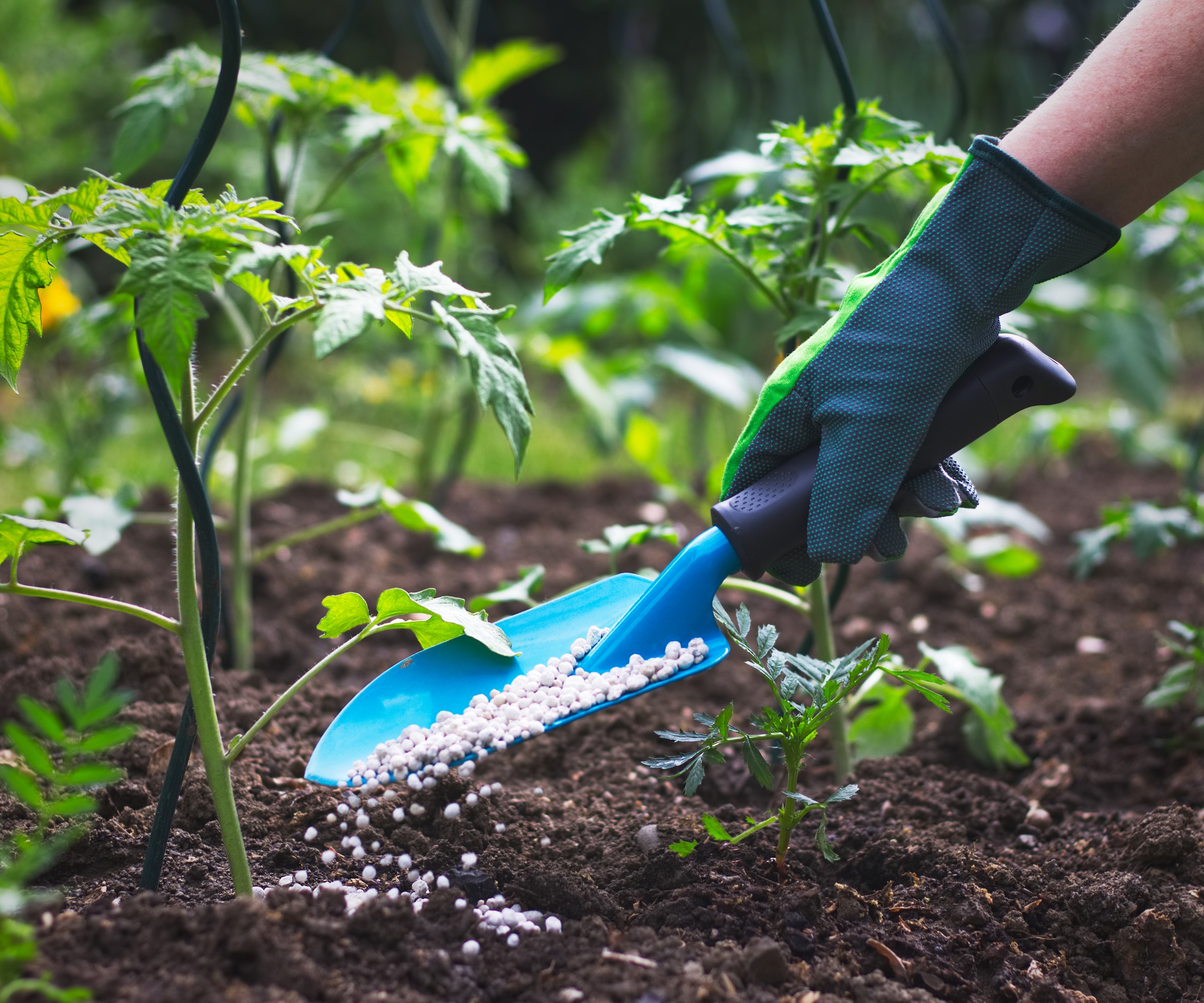

Granular fertilizer must be carefully sprinkled and incorporated into the soil

Drew is a former professional gardener who specialized in growing vegetables and fruit. He worked in kitchen gardens for the National Trust in the UK for several years and then ran a productive walled garden growing vegetables, fruit, herbs, microgreens, and flowers for chefs. He has used a wide range of fertilizers over the years, always making sure he is choosing the right one to target the specific needs of his varied plants and vegetable crops.
Plant fertilizer numbers explained
Fertilizer tends to come in two forms. A straight fertilizer contains just one of the essential plant nutrients of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, while compound fertilizers supply two or more of them.
The three major nutrients are always referred to as NPK. The content of nutrients is expressed on the bag, bottle, or box, in the order of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K). However, the packaging may not actively reference NPK but will always carry the three numbers, separated by dashes.
This indicates the nutrient content make-up. For example, 20-10-10 denotes a fertilizer that is 20 percent N, 10 percent P, and 10 percent K. The higher the number is, the more concentrated that particular nutrient is in the fertilizer.
Whether you're fertilizing evergreens, flowers or crops in your kitchen garden, it is important to always apply fertilizer at the recommended rate from the manufacturer as over-application can potentially kill plants.
Design expertise in your inbox – from inspiring decorating ideas and beautiful celebrity homes to practical gardening advice and shopping round-ups.
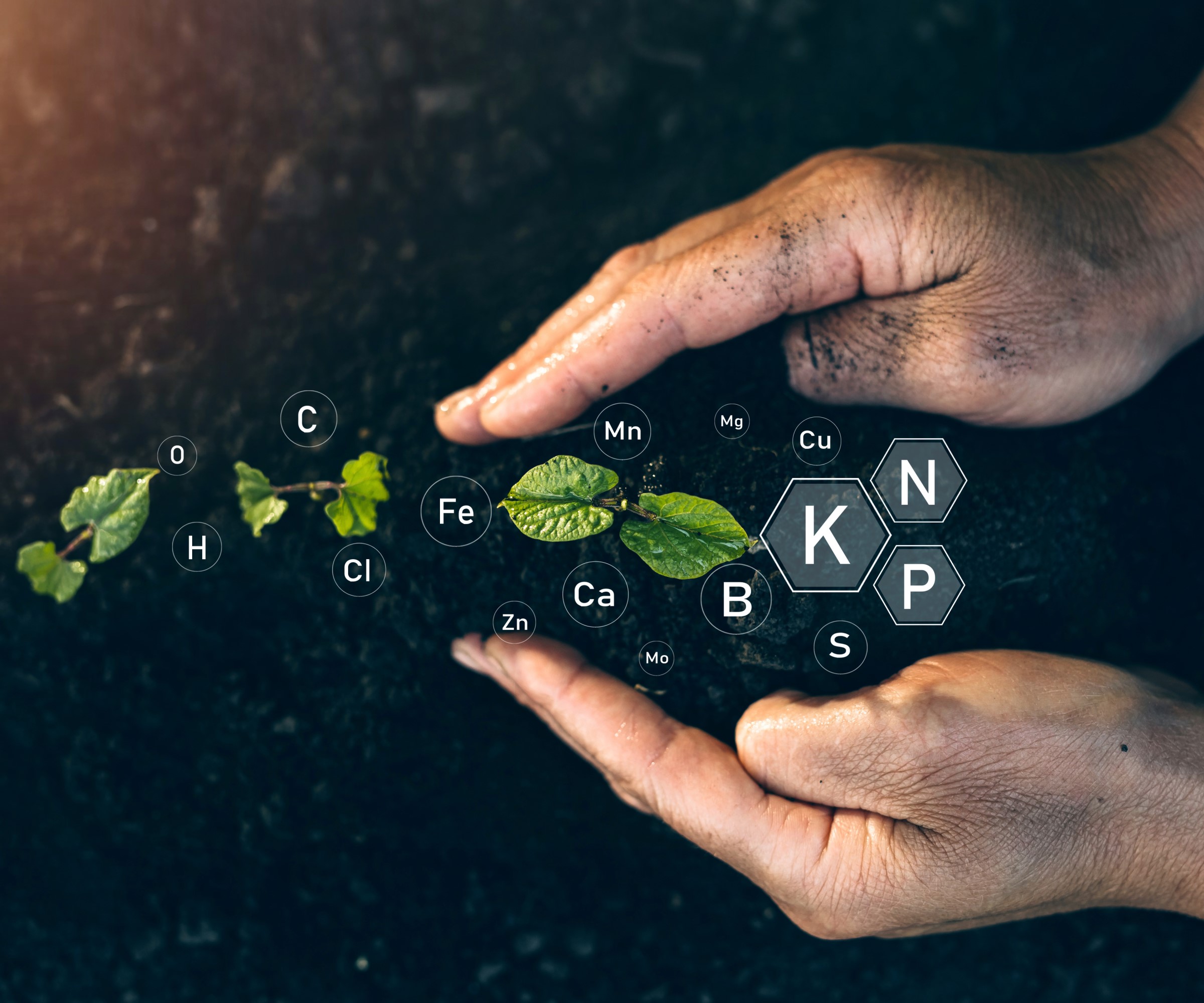

NPK are the 3 most important nutrients for healthy plants
Why is NPK important for plants?
NPK is important because plants need these three macronutrients to grow and a deficiency in any of these can cause your plants to struggle. Each one of NPK is vital for a different facet of a plant’s growth and not all plants will have the same requirements when it comes to nutrients. Therefore, understanding NPK and what it offers is vital to ensuring you are targeting any plant with the correct fertilizer. It is recommended to get your soil type tested to get a full understanding of its make-up and nutrient levels. Soil test kits are available at Amazon.
A balanced fertilizer is one with an equal amount of NPK, such as 10-10-10. Not all fertilizers are balanced as you can get targeted fertilizers with a higher make-up of specific nutrients. This could be for specific crops, for example plants in the vegetable garden might be grown for foliage and therefore need more nitrogen, or due to circumstances, such as if your soil already has a high level of one nutrient.
It is incorrect to assume that all-purpose plant foods are going to be balanced, for example the Miracle-Gro Water Soluble All Purpose Plant Food at Amazon has a ratio of 24-8-16. This ratio fits into previous studies that found the ideal nutrient ratio for flowering plants is 3-1-2. The Expert Gardener All-Purpose Water Soluble Plant Food Fertilizer from Walmart also has an NPK of 24-8-16.
What does nitrogen (N) do for plants?
Nitrogen is primarily responsible for vegetative growth as it plays a vital role in the production of chlorophyll. High-nitrogen fertilizers are given to plants or crops where leaf production is the most important, rather than for fruit, flower, or root crops.
An excess of nitrogen produces lush growth and can lead to the plants being more vulnerable to pests. A deficiency of nitrogen can see plants have yellowing of their leaves. Examples of high-nitrogen fertilizers include this chicken manure at Amazon and blood meal at Burpee.
What does phosphorus (P) do for plants?
Phosphorus is contained in large quantities within soil, though only a fraction of this is actually available to plants. It is a nutrient that is key for root growth, and flower and fruit development. It also helps with photosynthesis and crops maturing at the right time.
Phosphorus is really important for young plants as the nutrient is recycled from older parts to newer growing sections of the plant. Younger plants have a higher phosphate requirement than older ones. Signs of a deficiency include slow growth of the plant and yellow foliage.
Examples of fertilizers high in phosphorus include bone meal from Burpee, rock phosphate, and fish meal, so keep these in mind if you want to find ways of adding phosphorus to your soil, especially if you're facing a phosphorus deficiency.
What does potassium (K) do for plants?
Potassium plays an important role in the overall health of the plant and its metabolism. It is regarded to play a key part moving water and nutrients around the plant tissue.
Potassium also regulates the opening and closing of stomata to help the exchange of water, oxygen, and carbon dioxide. Leafy crops tend to take up a lot of potassium, especially when they are given high levels of nitrogen.
A plant with a lack of potassium can show signs of yellow leaves, brown leaf edges, and poor fruiting or flowering. Examples of fertilizers with higher levels of potassium include potassium sulphate available at Amazon, granite dust, and wood ash.

Only apply any fertilizer at the recommended rate
Other ingredients in fertilizers
Most fertilizers also contain additional ingredients or nutrients. This includes further nutrients such as magnesium, calcium and iron that are all important for healthy plant growth. It often also includes some organic matter or other filler material to bulk out the fertilizer. The exact make-up of the fertilizer should all be included on the label.
FAQs
What are the best NPK numbers for flower fertilizer?
The best fertilizers for flowers are all-purpose fertilizers that contain higher amounts of phosphorus. You are looking for fertilizer numbers where the second number on the fertilizer label is higher than the other two. This will boost the blooms in your flower bed.
What fertilizer number is best for growing plants?
A balanced fertilizer such as a 5-5-5 or 10-10-10 tends to be a good option for most plants. The same can be said of the all purpose plant foods with a 24-8-16 that are designed with that ratio in mind to be perfect for flowering plants. These will promote strong growth and happy plants as it caters for all the plant’s needs. However, it is not a one-trick fix and it pays dividends to look for fertilizers that are more targeted to what your plants need. For example, if you want leafy growth aim for more nitrogen, or go for a higher phosphorus fertilizer for flowers or fruits.
What happens if you give a plant too much fertilizer?
Plants that have been over-fertilized can show faltering signs, from wilting to their leaves looking brown and burned. Too much fertilizer can lead to a high concentration of salt in the soil that is taken up into the plant. This can burn the plant as the roots will be damaged and it cannot take in enough water to flush out the salts. If plants show signs of being over-fertilized, flood the area with lots of water to try to flush the fertilizer deep into the soil and away from the roots.

Drew has worked as a writer since 2008 and was also a professional gardener for many years. As a trained horticulturist, he worked in prestigious historic gardens, including Hanbury Hall and the world-famous Hidcote Manor Garden. He also spent time as a specialist kitchen gardener at Soho Farmhouse and Netherby Hall, where he grew vegetables, fruit, herbs, and cut flowers for restaurants. Drew has written for numerous print and online publications and is an allotment holder and garden blogger. He is shortlisted for the Digital Gardening Writer of the Year at the 2025 Garden Media Guild Awards.