Lavender growing mistakes – the 6 biggest errors to avoid, according to a gardening expert
This famous herb can be grown successfully if you steer clear of these common problems


Design expertise in your inbox – from inspiring decorating ideas and beautiful celebrity homes to practical gardening advice and shopping round-ups.
You are now subscribed
Your newsletter sign-up was successful
Want to add more newsletters?
Twice a week
Homes&Gardens
The ultimate interior design resource from the world's leading experts - discover inspiring decorating ideas, color scheming know-how, garden inspiration and shopping expertise.

Once a week
In The Loop from Next In Design
Members of the Next in Design Circle will receive In the Loop, our weekly email filled with trade news, names to know and spotlight moments. Together we’re building a brighter design future.

Twice a week
Cucina
Whether you’re passionate about hosting exquisite dinners, experimenting with culinary trends, or perfecting your kitchen's design with timeless elegance and innovative functionality, this newsletter is here to inspire
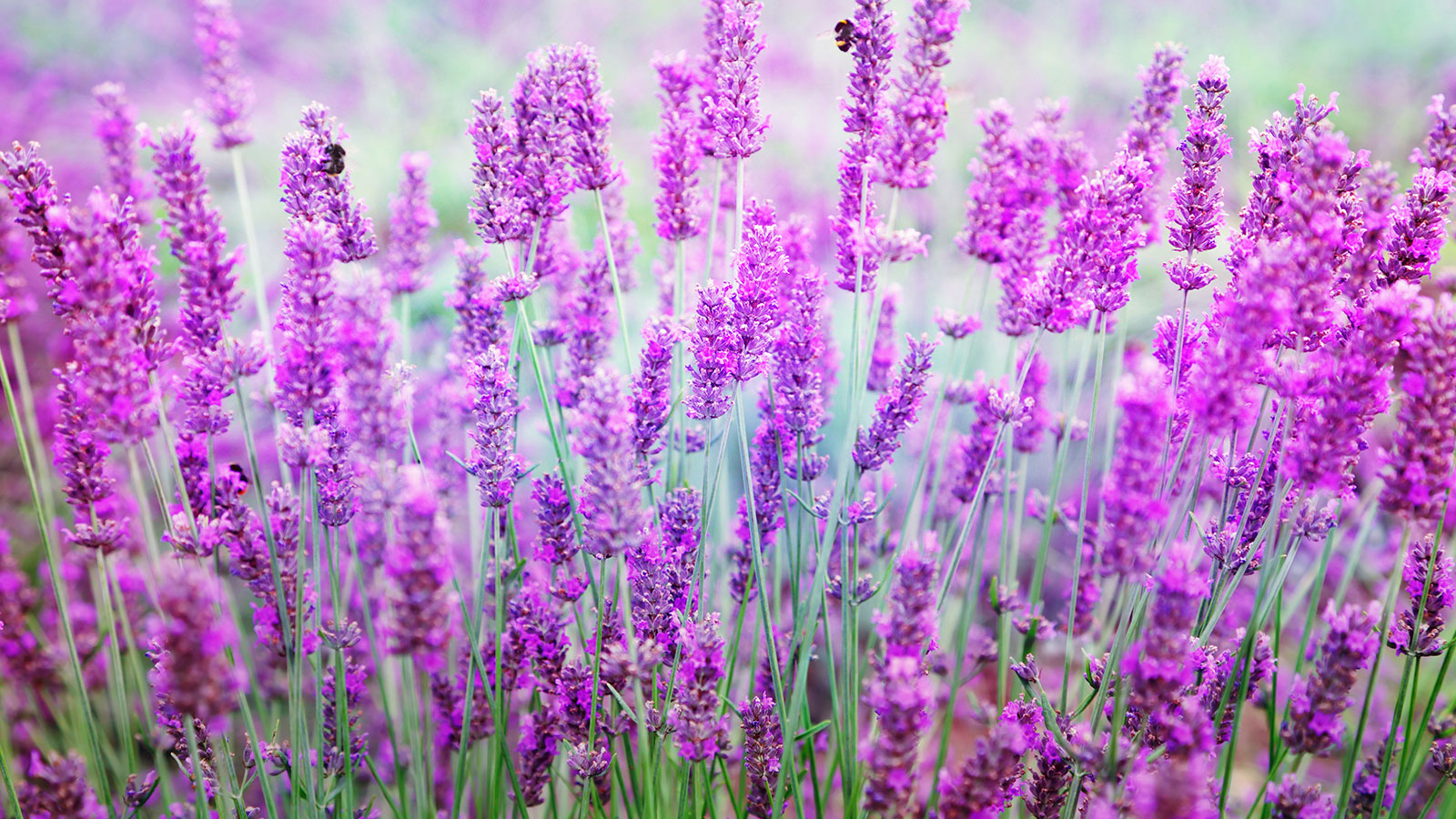
If they are planted in the right place and given the right care, lavender bushes can last for years, but they are quick to fail if they are not happy.
With its grey-green leaves, striking pink and purple flowers and distinctive scent that has been loved for generations, lavender is one of the most recognisable shrubs to grow. Loved for it herbal uses and aesthetic charm for centuries, it is a favorite for many gardeners.
For all of those reasons and more, I've grown lavender in my own garden for many years. However, experience has taught me that there are several common mistakes that can prevent your lavender plants from thriving.
6 lavender growing mistakes you need to avoid
These are the top six reasons why lavender plants fail, plus my tips for avoiding them so you can successfully grow this shrub in your herb garden.
1. Choosing the wrong variety
In spite of its Mediterranean roots, lavender can grow in US hardiness zones 4-10. However, some varieties are more frost-tender, while others are susceptible to excessive heat and humidity, which can cause fungal problems, so for this reason you need to choose the variety that will thrive best in you garden
You may need to winterize lavender to help it through the coldest months when they go dormant. Some of the hardier varieties, such as English lavender, can survive winters where the temperatures fall to -20˚F, whereas others will only survive down to 20˚F or 30˚F.
There are three main types of lavender and you should choose the one that will suit your climate the best to avoid making a lavender growing mistake:
Design expertise in your inbox – from inspiring decorating ideas and beautiful celebrity homes to practical gardening advice and shopping round-ups.
- English lavender: Cultivars of Lavandula angustifolia are characterised by their narrow, scented flowerheads that range in color from darkest purple to pale mauve. They are hardy and can overwinter in growing zones 5-8. However, gardeners in the north may wish to protect plants with a thick layer of mulch over the roots and use frost protection such as fleece insulation for the main plant like these frost blankets available on Amazon when very harsh winter weather is forecast.
- French/Spanish lavender: Lavandula stoechas can be recognized by the 'tufts' pf petals emerging from the top of the hard, elongated flower heads. These types are not as hardy as English varieties and are ideal for gravel gardens and container gardening (as the best soil for lavender is free-draining). In hardiness zone 7 and warmer, they will flower all summer and well into the fall.
- Hybrid lavenders: Lavandins are hybrids of English lavenders and are grown throughout southern France for their strong scent and oils, which are widely used in the perfume industry. They have long, loose-growing stems with tapering flowers and grow well in hardiness zones 5-10.
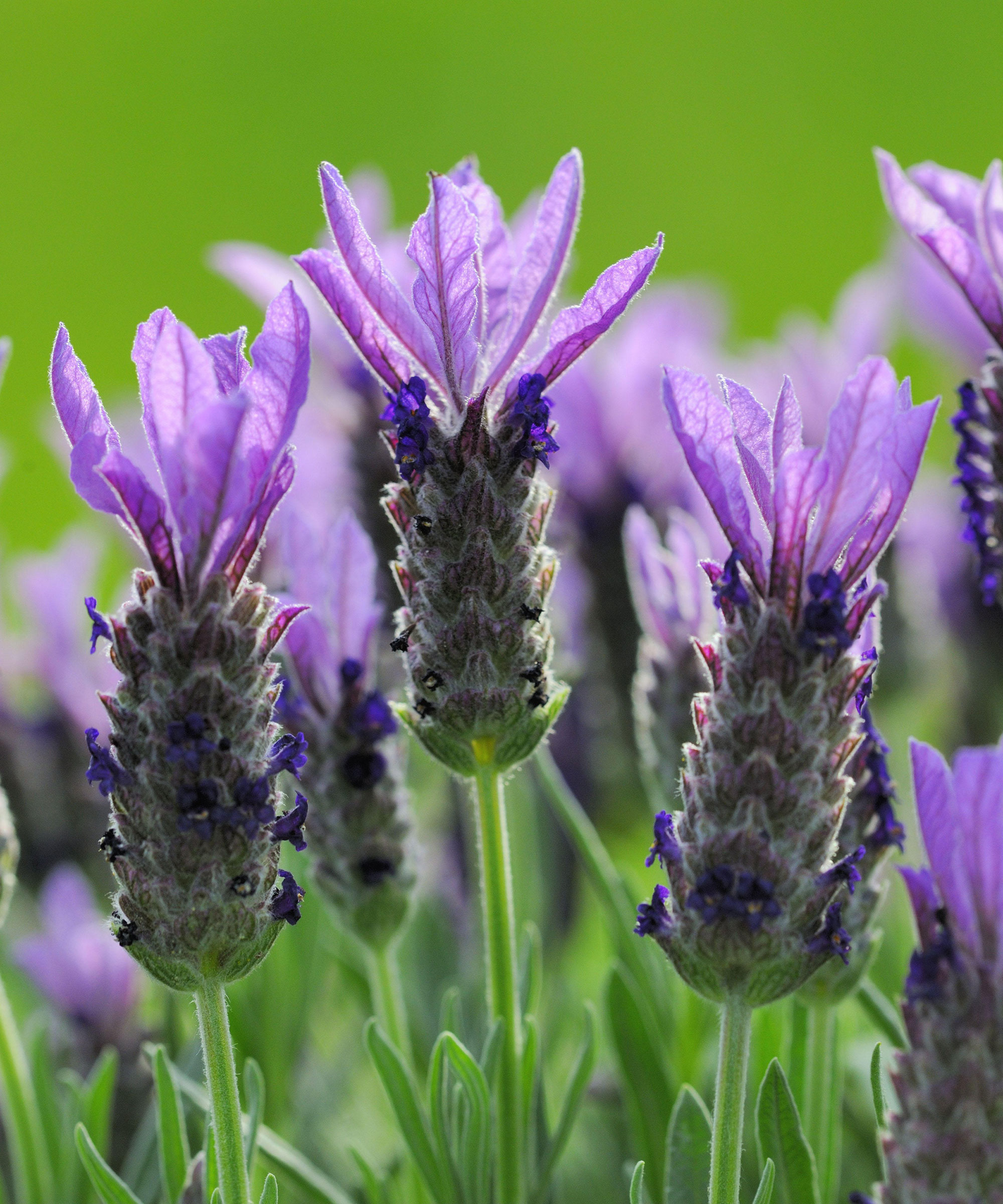

French or Spanish lavender (Lavandula stoechas) is not as frost-hardy as some varieties
2. Overwatering lavender
Lavender hails from the Mediterranean where it thrives in the dry heat and poor soil. Despite its elegant appearance and wealth of scented blooms, it doesn't need much watering and lavender is drought tolerant – in fact if you are too generous when watering lavender you can cause the roots to rot and kill the plant.
You should also take into account what soil type you have when planting lavender. The best soil for lavender is free-draining, gritty soil that drains fast, but if your yard is on clay we would recommend digging a planting hole 2-3 times as big as the plant’s rootball, then breaking up the sides and base with a garden fork.
If you don’t do this, the hole can become a 'bucket', holding on to water instead of letting it drain away, and this is more likely to cause root rot. This can lead to additional lavender pests and problems.
Before planting your lavender in clay soil, add some compost like this Ribbons Organic Compost on Amazon and grit such as Garden Pummice, available on Amazon, to the planting hole to further improve drainage and keep the lavender roots healthy.
If your soil is very heavy, or you don’t have the space to plant in a border, add lavender to your herb planters, containers and vegetable garden containers.
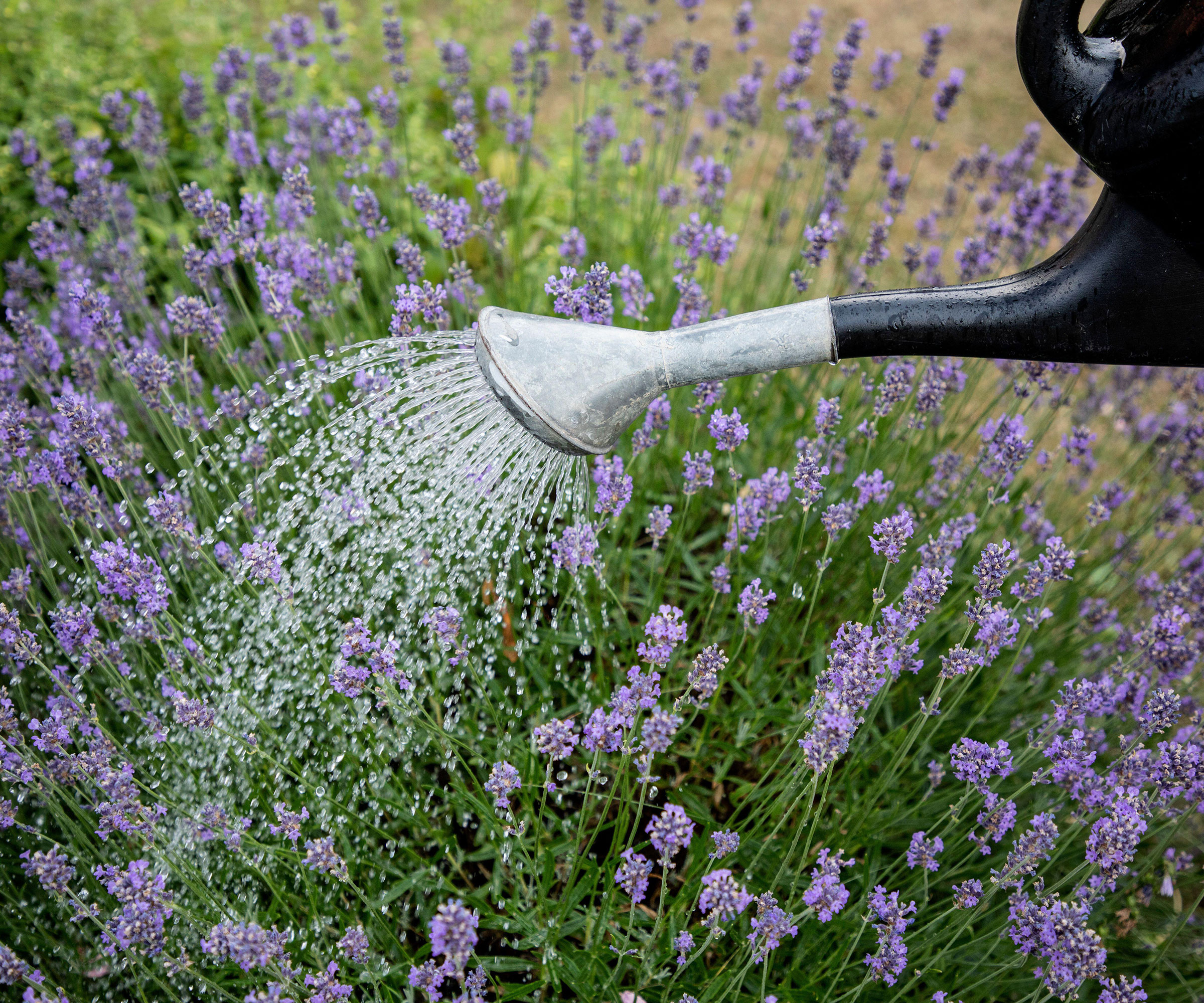

Lavender needs very little moisture and overwatering can rot the roots and kill the plants
3. Overfeeding lavender
Overfertilizing lavender is as bad as overwatering it, and another common mistake that can cause your plants to fail.
Like many woody-stemmed Mediterranean herbs, including sage and thyme, lavender has evolved to grow well in poor, dry soil. Too much fertilizing, especially with a nitrogen-rich fertilizer, can cause the plants to produce excessive amounts of leaves and not many flowers.
This soft growth is also more at risk of contracting fungal diseases such as powdery mildew because a proliferation of stems blocks healthy ventilation, and is more likely to be attacked by pests.
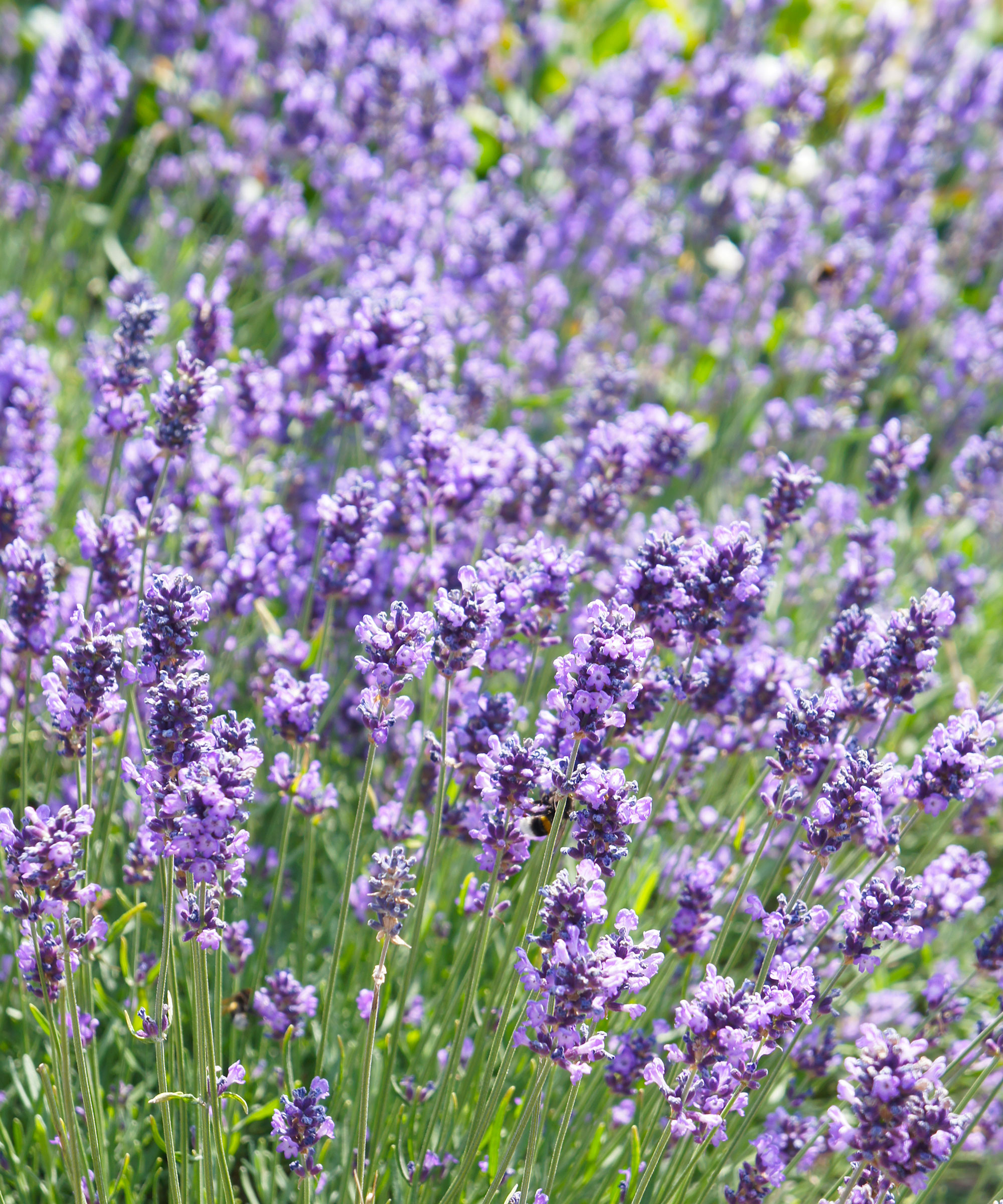

Lavender doesn't need extra fertilizing to keep it growing strongly
4. Planting in shade
Lavender evolved to thrive in hot Mediterranean sunshine, so grow it in the sunniest place in your yard. The plants need 8-10 hours of sunshine to do their best, and if you plant them in shade their famous scent won’t be as strong.
When you plant your little lavenders, whether they will be single plants or used as a border to a pathway or a scented low-growing hedge, make sure they have plenty of room and are not likely to get overshadowed in the future as the surrounding plants grow larger.
If you are not sure which is the best area for growing lavender, try sun-mapping your garden – it is easier than you think.
The best place for them is a south-facing area of your garden that gets the most sun, a gravel garden where they have space to flourish away from other plants that may cast a shadow, or a Mediterranean garden border with lots of similar sun-loving plants that have the same care requirements.
If you have planted your lavender in the wrong place don't panic. The best time to transplant lavender is in spring or fall when the soil is warm and damp, though this works best for young plants.
If your lavender has grown old and woody it is unlikely to relocate as successfully, so take plant cuttings and make new plants that can grow in a sunny, free-draining spot in your yard.

Lavender needs an open space and no shade and is perfect for a gravel garden
5. Planting too close together
Lavender bushes can become quite large so they need enough space to help them grow healthily and reach their full potential. If they are grown too close together, your lavender is at increased risk of fungal diseases caused by poor airflow. Plants crammed together also make it easier for pests to travel from one to another.
And while lavenders do thrive in poor soil, if you have several plants growing in close proximity they will be competing for water, nutrients and sunlight and may fail to thrive.
You can buy lavender as small plug plants or as larger shrubs. The best time to plant is April and May when the soil is damp from spring showers, and warming up after winter.
If you are planting a group of lavenders in a flower bed, set them 3ft apart – it sounds a lot but in the right conditions they will soon grow to fill the space.
If you are planting lavenders as low-growing hedging plants, place the plants 1ft apart and they will quickly fill out and form an attractive scented barrier.
If you are planting lavender in a container, use free-draining potting soil and add some horticultural grit or gravel to further improve the drainage.
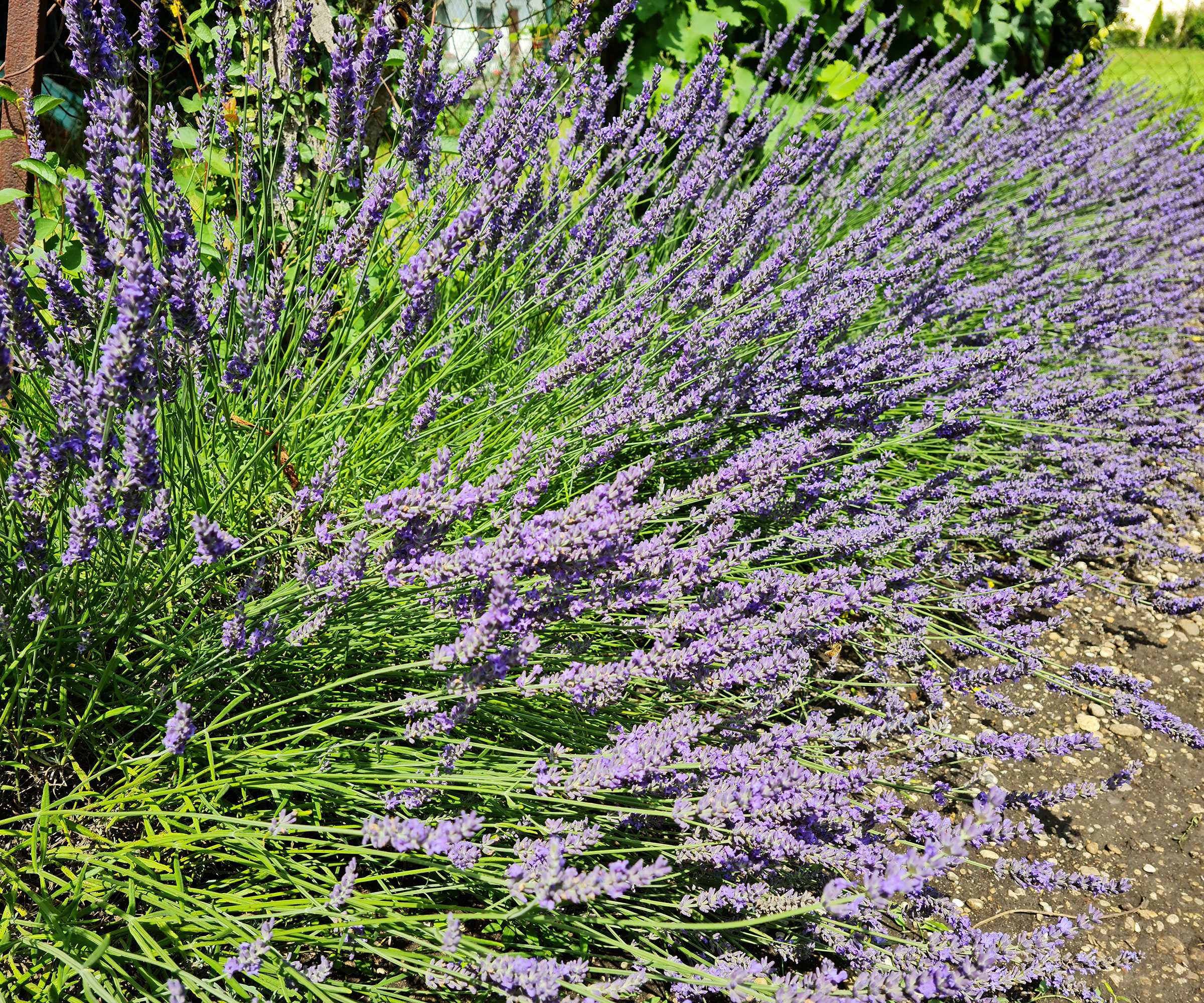

Give lavender shrubs the space they need to grow well
6. Getting pruning wrong
Once your lavender is established it will need pruning each year. How to prune lavender depends on the variety you have and the age of the plant. Get it right and you will create attractively shaped mounds with plenty of scented flowers, but prune badly and you risk being left with leggy, woody skeletons with little visual appeal and reduced flowering.
Small or single bushes can be tackled with pruners, such as this excellent value four-pack of Kotto tools and gloves on Amazon, while it can be easier to prune larger shrubs or a collection of plants with shears, like this Gardena hedge shears, also on Amazon.
Make sure they are sharp or the blades will crush and bruise the stems, and always clean your tools well after use.
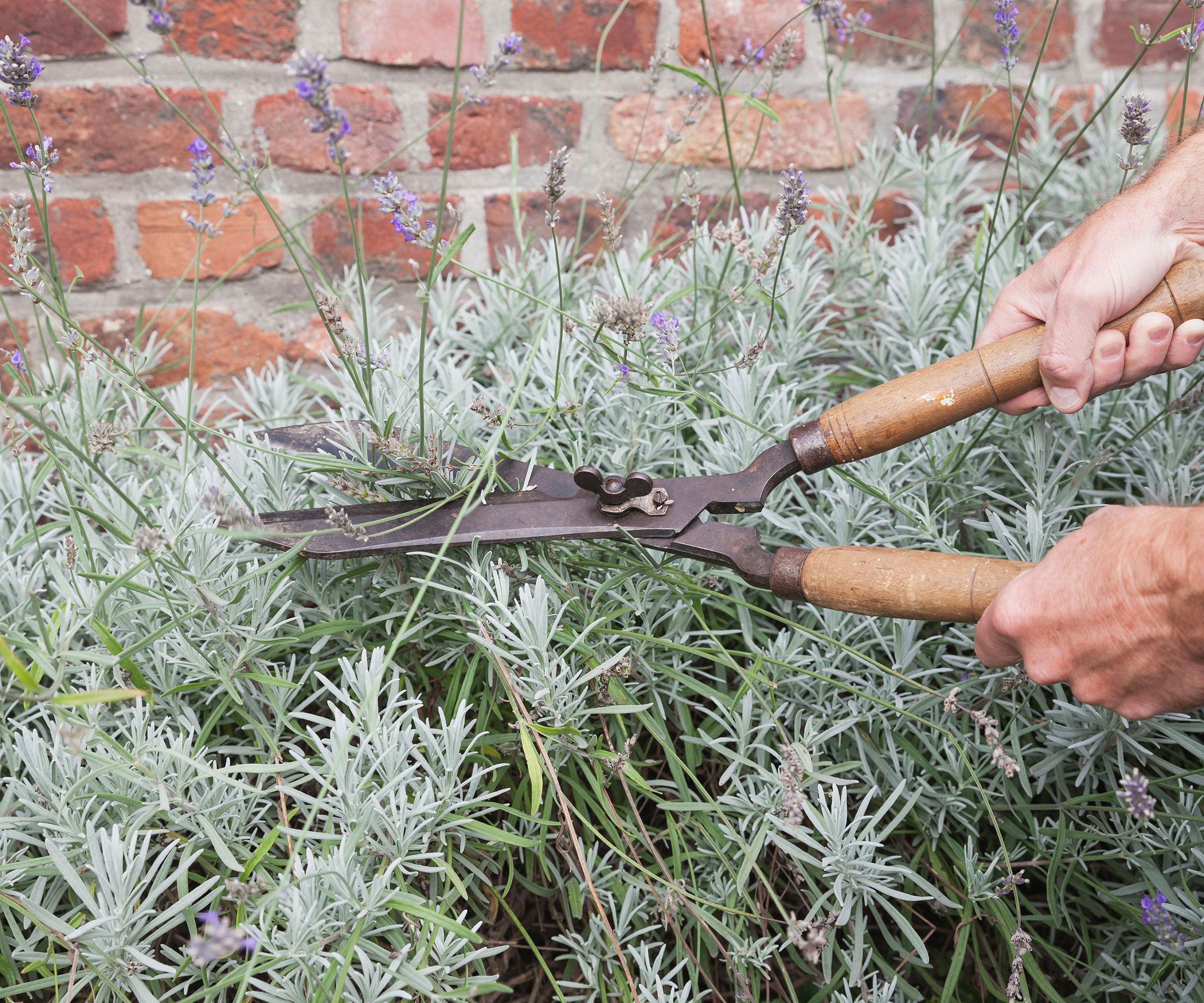

Shears are the best way to remove stems on large lavender bushes
One of the best reasons for growing this low-maintenance shrub is so you can learn how to harvest lavender flowers for drying to use in pot pourri, or to dry flowers for use in flower arrangements and even as edible cake decorations.
By avoiding the most common lavender harvesting mistakes and harvesting it at the right time, you will find this popular plant has a wealth of uses.

Ruth is a Contributing Editor for Homes & Gardens, and formerly Gardening Editor of Amateur Gardening magazine. She is horticulturally trained, with a qualification from the Royal Horticultural Society. Her work for Amateur Gardening, the world's oldest weekly gardening publication, involved matching gardening tasks with each season, covering everything from sowing and planting, to pruning, taking cuttings, dealing with pests and diseases and keeping houseplants healthy. She is an expert in ornamental plants and edible crops, and everything she writes about and photographs is in her own garden, that has been a work in progress since her family moved there in 2012.